Hyperlipidemia is a term you may have heard when talking about cholesterol, but what exactly does it mean? Hyperlipidemia occurs when the blood has elevated lipids (fats) levels - primarily cholesterol and triglycerides. This can be caused by underlying health conditions and lifestyle habits such as dietary intake of fat, lack of physical activity, and obesity.
If left untreated, Hyperlipidemia can increase cardiovascular disease risk, including heart attack or stroke. This blog post'll explore more detailed information on what causes Hyperlipidemia, its symptoms, and available treatments.
What Is Hyperlipidemia?
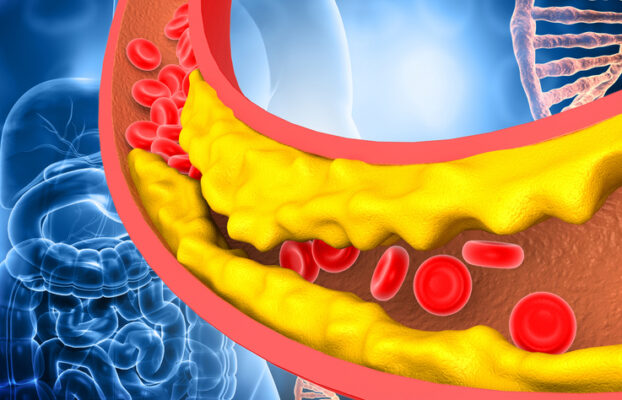
Hyperlipidemia is a medical condition characterized by high levels of lipids in the blood, such as cholesterol and triglycerides. It is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, stroke, and other health issues. The underlying cause may be genetic or related to lifestyle factors like diet and exercise habits.
People with Hyperlipidemia should talk to their healthcare provider about lifestyle changes, medications, and regular monitoring to help manage their condition. Treatment can help reduce the risk of developing serious health issues. While Hyperlipidemia cannot be cured, lifestyle modifications and proper management can help control it.
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Artery disease
Types of Hyperlipidemia
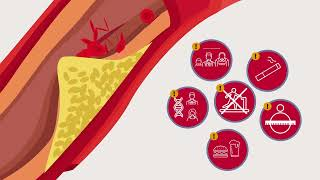
- Acquired Hyperlipidemia Sometimes, certain behaviors or the lack of them can cause the disease. In other cases, it can be caused by medicine or other health problems. Additionally, some people can inherit the disease from their parents.
- Familial hypercholesterolemia One type of genetic Hyperlipidemia is characterized by a gene mutation that results in cholesterol accumulation on artery walls instead of being removed from the body.
- Familial hypertriglyceridemia is a genetic condition that results in elevated levels of triglycerides.
How common is Hyperlipidemia?
Hyperlipidemia is a very common condition. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, about one in three adults has high blood cholesterol. High cholesterol increases the risk of developing heart disease, stroke, and other serious medical conditions. Therefore, it is important to be aware of your cholesterol levels and take steps to manage them if they are too high.
Understanding what Hyperlipidemia is and how it can be managed is also important. Hyperlipidemia is characterized by high levels of lipids, or fats, in the blood. These fats include cholesterol and triglycerides. High levels of these substances can increase the risk for atherosclerosis or plaque buildup in your arteries, restricting blood flow to organs and tissues. This can lead to a heart attack or stroke if left untreated.
How does Hyperlipidemia affect my body?
Hyperlipidemia, sometimes referred to as high cholesterol, is a disorder in which the blood has excessively high levels of certain lipids (fats). Triglycerides, cholesterol, and other fatty acids are some of these lipids. You run a higher risk of developing cardiovascular conditions like a heart attack and a stroke if you have high amounts of these lipids.
Heart attack, stroke, carotid artery disease, sudden cardiac arrest, peripheral artery disease, and microvascular disease are among the illnesses.
What causes cholesterol to get high?
Various hyperlipidemia causes include:
- Smoking.
- Drinking a lot of alcohol.
- Sitting too much instead of beings actively.
- Being stressed.
- Inheriting genes that makes the cholesterol levels unhealthy.
- Being overweight.
Medical problems can also affect how much cholesterol you have. These include:
- Diabetes.
- Kidney disease.
- Hypothyroidism.
These problems make it hard for your body to naturally remove cholesterol from the blood.
What are the risk factors for Hyperlipidemia?
The most common risk factors for Hyperlipidemia include: being overweight or obese, having an inactive lifestyle, consuming high-fat and processed foods, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain medical conditions such as diabetes and kidney disease. Additionally, some medications may also increase the risk of developing Hyperlipidemia.
To reduce your risk of developing Hyperlipidemia, it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise and a balanced diet with plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables. Additionally, monitoring your cholesterol levels and blood pressure regularly is important. If your doctor determines that you are at risk for developing Hyperlipidemia, they may recommend certain lifestyle changes or medications to help keep your cholesterol levels under control.
It is important to note that Hyperlipidemia is often linked to other medical conditions. You should speak with a healthcare professional about the best ways to reduce risk and manage the condition if necessary. Keeping your cholesterol within a healthy range can reduce your risk of developing further complications from Hyperlipidemia.
How is Hyperlipidemia (high cholesterol) diagnosed?
A blood test called a lipid profile is commonly used to diagnose hyperlipidemia (high cholesterol). This examination evaluates the blood's levels of triglycerides, LDL ("bad") cholesterol, HDL ("good") cholesterol, and total cholesterol.
An increased risk of getting heart disease is indicated by any of these readings that are higher than average. To assist lower your cholesterol levels and lessen risk, your doctor may advise medication or lifestyle modifications.
Talk with your doctor about the best option for you.
Also, remember that diet and exercise play a large role in managing cholesterol levels. Eating a healthy diet and participating in regular physical activity can help reduce your cholesterol and improve your overall health.
Talk with your doctor for more information on how to make these healthy lifestyle choices. These changes can help lower your risk of heart disease and other conditions associated with high cholesterol.
What are the symptoms of Hyperlipidemia?
The most common symptom of Hyperlipidemia is an elevated level of lipids, or fats, in your blood. This can be determined through a simple blood test. Additional symptoms include chest pain, abdominal pain, and fatigue.
In rare cases, individuals may experience yellow fatty deposits on their eyes or skin due to high body fat levels.
It’s important to note that even if you don’t experience any of these symptoms, you may still be at risk for Hyperlipidemia. Regular checkups with your doctor can help identify any changes in your lipid levels before they become a significant health risk.
FAQs
How do you fix Hyperlipidemia?
The treatment for Hyperlipidemia is based on your risk factors and the severity of your condition. Generally, lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet and regular exercise are recommended as the first defense against high cholesterol levels. Your doctor may also prescribe medications to help lower cholesterol levels if necessary.
Some dietary supplements can also be beneficial in managing Hyperlipidemia, but it is important to discuss these options with your doctor before taking them. Finally, quitting smoking will help reduce your risk of developing heart-related problems associated with Hyperlipidemia.
Do eggs increase your cholesterol?
Eggs contain cholesterol but are also a good source of protein and vitamins. Eating eggs in moderation, such as one to three per day, is generally considered safe and can be part of a healthy diet that includes other sources of dietary cholesterol. However, following your doctor's advice regarding egg consumption is best if you have high cholesterol or are at risk for developing Hyperlipidemia.
What are 5 foods that can lower cholesterol?
Foods that can help lower cholesterol include oats, legumes, nuts, fatty fish, and olive oil. Oats contain a soluble fiber called beta-glucan which helps to reduce bad cholesterol levels. Legumes such as beans and lentils are also high in fiber and can help lower cholesterol.
Nuts, such as almonds or walnuts, contain healthy unsaturated fats that help to reduce LDL cholesterol. Fatty fish, such as salmon or tuna, are rich in omega-3 fatty acids that can decrease bad cholesterol. Finally, olive oil is a healthier source of monounsaturated fats which can help reduce LDL levels.
Conclusion
In Conclusion, Hyperlipidemia is characterized by high levels of fats and cholesterol in the blood. It has many potential causes, including genetic factors, diet, lifestyle, medications, or certain medical conditions. Left untreated can increase your risk for serious health complications like stroke and heart disease.
The best way to prevent and managHyperlipidemiaia is to make healthy lifestyle choices, such as eating a balanced diet and exercising regularly. It's also important to talk to your doctor regularly to discuss your options and monitor potential risks.