Histamine intolerance, a condition where the body struggles to break down histamine properly, can lead to a host of uncomfortable symptoms, including hives, headaches, and digestive issues. While it's not possible to follow a completely histamine-free diet, identifying and avoiding foods with high histamine levels or those that trigger its release is crucial for managing symptoms. However, navigating dietary choices can be challenging, as histamine is present in many common foods. In this comprehensive guide, we'll take a closer look at eight specific foods that individuals with histamine intolerance might consider limiting or excluding from their diet altogether to maintain wellbeing and alleviate the discomfort associated with this condition.
What is Histamine Intolerance?
Histamine intolerance is a condition where the body's natural process of breaking down histamine, a chemical involved in immune response and digestion, is impaired. This can be caused by a deficiency in the enzyme diamine oxidase (DAO) or other factors, leading to an accumulation of histamine in the body.
Symptoms of histamine intolerance can vary from person to person but may include headaches, difficulty breathing, hives, digestive issues such as diarrhea or constipation, and skin irritations. These symptoms are a result of histamine's effect on the body's tissues and its involvement in allergic reactions.
8 Foods to Avoid with Histamine Intolerance
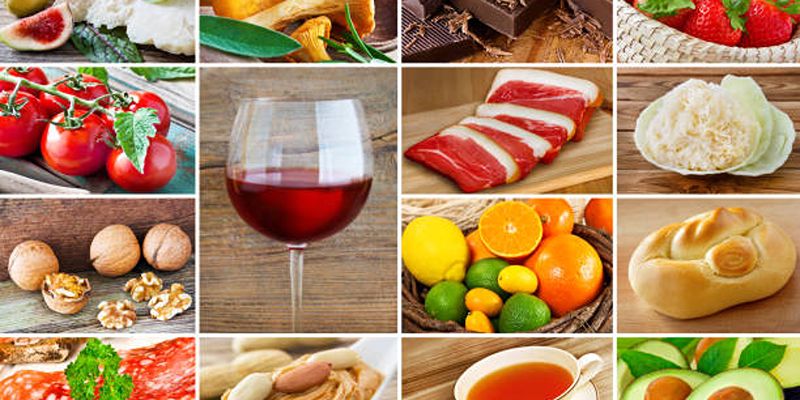

1. Fermented Foods
Fermented foods are products of a rich, ancient tradition of food preservation that enhances flavor and increases shelf life. Unfortunately, for individuals with histamine intolerance, these same foods can be problematic. Fermentation enables the growth of bacteria and yeast that produce histamine as part of their metabolic process. Common fermented foods include aged cheeses, sauerkraut, kimchi, soy sauce, and yogurt. These items can be high in histamine or act as histamine liberators, potentially exacerbating symptoms in sensitive individuals. Consequently, ferment-loving gourmands with histamine issues might need to find alternatives that satisfy their palate without compromising their well-being.
2. Processed and Cured Meats
Processed meats such as bacon, salami, and deli meat are typically high in histamine. These foods are preserved using a curing process that involves fermentation or aging, making them risky for individuals with histamine intolerance. Furthermore, the addition of preservatives like nitrates and sulfites can also contribute to histamine levels in these meats.
3. Citrus Fruits
Although citrus fruits like oranges, lemons, and grapefruits are generally considered healthy options for most people, they can be problematic for individuals with histamine intolerance. These fruits contain high levels of naturally occurring histamines that can trigger symptoms in sensitive individuals. They also have a compound called limonene, which can block DAO enzymes and impair histamine breakdown. As a result, people with histamine intolerance may want to avoid or limit citrus fruits in their diet.
4. Artificial Food Colorings and Preservatives
Artificial food colorings and preservatives are prevalent in many processed foods and can be a hidden source of histamine issues. These additives can trigger the release of histamine from mast cells in the body, exacerbating symptoms for those with histamine intolerance. Foods laden with artificial dyes, benzoates, sulfites, and nitrites should be approached with caution. Reading labels carefully and choosing fresh, unprocessed food can help individuals with histamine intolerance avoid these problematic ingredients.
5. Tomatoes
Tomatoes are a staple ingredient in many cuisines around the world. However, for individuals with histamine intolerance, this popular fruit can be problematic. Tomatoes are naturally high in histamine, and they also contain lycopene, a compound that can inhibit DAO activity. Furthermore, cooked tomatoes have higher levels of histamine than raw ones, making them even more problematic for people with histamine intolerance.
6. Spinach
Spinach, often hailed for its nutritional profile, is packed with vitamins and minerals essential for maintaining good health. However, it can be less than ideal for those with histamine intolerance. This leafy green is considered a histamine liberator— meaning that consuming spinach can trigger the body to release its own histamine stores, which may worsen symptoms for individuals with the condition. While cooked spinach tends to be higher in histamine than its raw counterpart, both forms may need to be consumed with caution or avoided by those sensitive to histamine.
7. Chocolate
Chocolate, a beloved treat worldwide, can present challenges for individuals with histamine intolerance. Cocoa itself is a histamine liberator and chocolate, especially dark and aged varieties, contains significant amounts of histamine. Moreover, other ingredients commonly found in chocolate, such as nuts or soy lecithin, may exacerbate histamine response. While the idea of excluding chocolate from one's diet may seem disheartening, those with histamine intolerance might need to consider this step to reduce symptoms and maintain quality of life.
8. Strawberries

Strawberries may be small, but they pack a significant punch when it comes to histamine content. This seemingly innocent fruit can be quite deceiving for those with histamine intolerance as it not only contains histamine but has been noted to trigger histamine release in the body. Additionally, the red pigment in strawberries is thought to potentially block the action of DAO, the primary enzyme involved in breaking down histamine. This could exacerbate symptoms ranging from hives to respiratory issues. Those with histamine intolerance may experience relief by omitting strawberries from their diet and opting for low-histamine fruit alternatives.
Conclusion
Managing histamine intolerance involves avoiding or reducing the intake of histamine-rich foods. Making dietary changes can be challenging, but it can significantly improve symptoms and quality of life for individuals with histamine intolerance. Avoiding the foods listed above and replacing them with low-histamine alternatives may help reduce symptoms and enable individuals to enjoy a more comfortable and fulfilling diet. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before making significant dietary changes. A personalised approach based on individual needs and food tolerances is crucial for effectively managing histamine intolerance.